Save a memory block to disk
This article shows how to dump a a block of memory to a file, while debugging the program, without writing a debugging function into the program and without recompiling it.
Sample code
int main()
{
// buffer size
int bufferSize = 1024;
// create buffer
void* buffer = calloc(1, bufferSize);
// set some bytes into the buffer
memset(buffer, 0xAB, bufferSize);
// release memory
free(buffer);
return 0;
}
While this is a very simple piece of code, and writing a small function to save buffer contents
to disk is not such a big deal, for a more complicated program ( thousands of lines of code ),
if there isn’t already enough debugging code in place, we need to restart the debugging process every time
that we add some new debugging code.
VSDebugPro extension offers a simple solution for this:
dumpmem
Dump memory utility.
------------------------------------------------------------------
Syntax: <dumpmem> <optional flags> <filename> <address> <size>
EX: dumpmem c:\memdump.bin 0x00656789 200
EX: dumpmem -f c:\memdump.bin 0x00656789 200
Flags:
-f - Force file overwrite.
-a - Append to the file.
<filename> - output filename
<address> - read address, must be a hex address / pointer, can be an expression
<size> - size in bytes, can be an expression
------------------------------------------------------------------
Steps to dump buffer contents to disk:
- Start debugging the program.
- Place a breakpoint at a carefully select point in code, where our data is available.
- Go to VSDebugPro menu and open Console.
- Dump buffer contents with the following command:
dumpmem buffer.bin buffer bufferSize
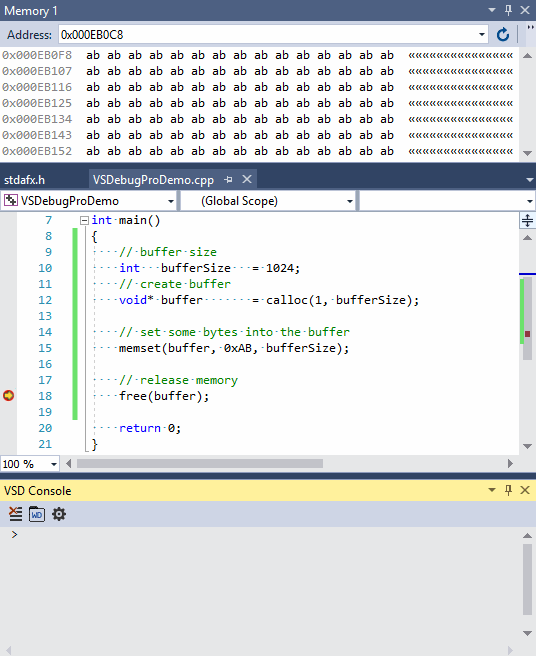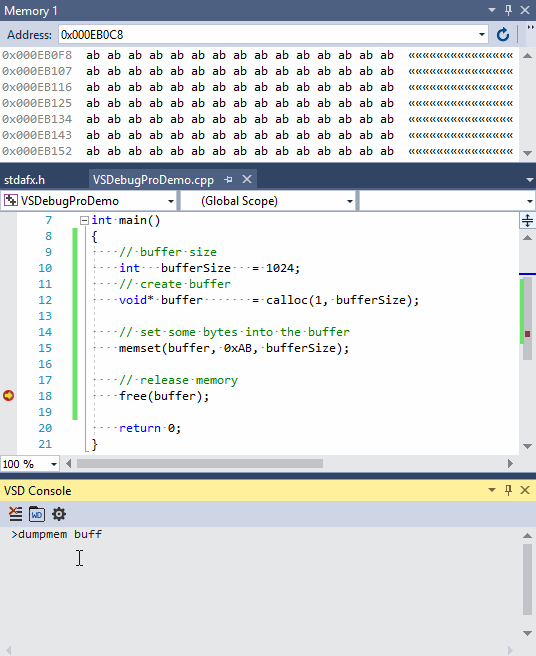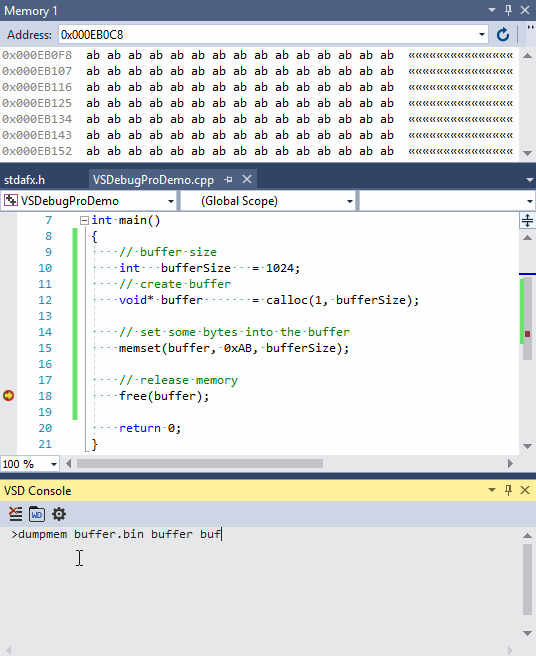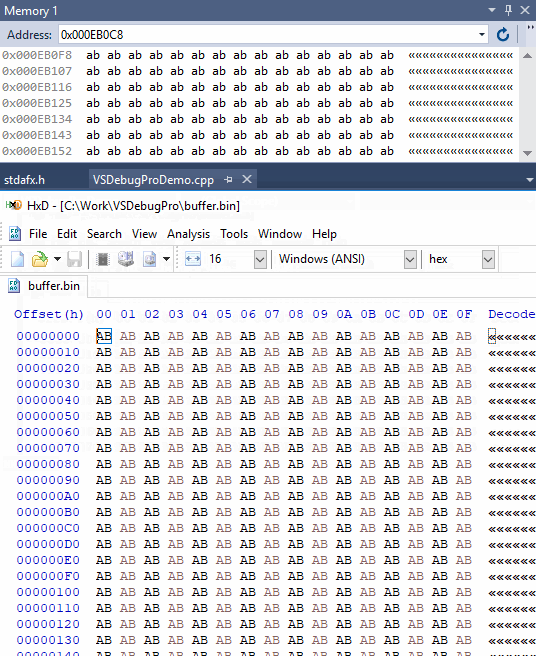
The dumpmem utility uses the Visual Studio C++ debugger interface to automatically evaluate
the address of buffer and the size from bufferSize variable.
References
HxD a free hex editor.